Do you know the real cost of project delays? For example, in the UK alone, government projects worth £200 billion are in red, which means that they are unfeasible, and plans are unachievable [1]. That’s a harsh truth for many organizations – they invest in projects but instead of gaining profit, only have missed due dates, bloated budgets, and blurred outcomes.
How can organizations break this vicious circle? One of the solutions is effective PMO risk management. It’s critically important for organizations managing multiple interconnected projects.
Read the article to learn why PMO risk management is important, what its key stages are, and how to implement it effectively.
What Is PMO Risk Management?
In simple words, PMO risk management is the process of administering risks by a project management office (PMO). If we expand on this topic a little bit, we’ll describe PMO risk management as applying processes, techniques, frameworks, and tools to identify, analyze, and mitigate risks across projects (programs, portfolio) that they are in charge of. Its main purpose is to minimize the impact of negative risks and maximize opportunities offered by positive risks. Compared to project risk management that deals with risks at the level of isolated projects, PMO risk management works on the organizational level. It means that it takes into account project interdependencies and their impact on risk management as well as organizational goals.
The main benefits of risk management performed by a project management office are as follows:
- It minimizes the risk of project failures thanks to early identification of negative risks and developing mitigation plans;
- It facilitates effective prioritization of projects in a portfolio, as potential risks are one of the prioritization criterion;
- It helps align projects with organizational goals.
Let’s consider the detailed role of PMO risk management in the section below.
The Role of the PMO in Risk Management
So, what is the contribution of a project management office to the enterprise-wide risk management?
Standardization of the risk management processes.
As we know, PMO is an organization that establishes standards for project, program, and portfolio management processes. And risk management is not an exception. Therefore, PMO is responsible for establishing a standardized risk management framework across projects, including developing methodologies, templates, and adopting tools for more effective risk administration.
Providing comprehensive visibility for effective risk management process.
As we’ve mentioned before, PMOs deal with risks at the level of the whole multi-project environment, especially if it’s an enterprise PMO. This is why they use specific techniques and tools to provide centralized visibility into risks and are responsible for risk management strategy across projects. Also, they perform risk analysis on the level of the whole project environment and provide executives with important insights into key risks that require their attention.
Risk monitoring and control.
In addition to risk analysis, PMOs should perform regular monitoring and control. For example, they collect possible risks, monitor threats with high impact, and cross-project risks. This not only helps stay informed regarding possible threats and be ready to respond to them in the most effective way but also maintain oversight of the entire project environment.
Giving grounds for decision-making.
The insights provided by a project management office facilitate making informed decisions by stakeholders and a company’s management. Decision support for risk management is no exception. For example, based on risk management insights, portfolio managers can adjust project priorities and reallocate resources.
But what are these risks that a typical PMO has to deal with? Let’s consider them in the section below.
What Are Common Risks Managed by PMOs?
Project management offices have to manage different types of risks. For convenience, we’ve classified them into several categories.
1. Strategic risks.
This group of risks embraces events that put at stake the alignment of projects and portfolios with organizational goals. For example, they may include prioritization mistakes or market changes. A lack of proper management of these risks can result in wasted project investments.
2. Financial risks.
As you can guess from the title, these risks refer to all financial issues: e.g., budget overruns, improper project funding, inability to achieve the expected return on investments. When unmanaged, these risks may result in financial losses, a lack of profitability, or cancelled projects.
3. Technical risks.
It’s hard to imagine project management without using technology. A great number of projects across industries require equipment of software tools. Of course, they can go out of service while a project is underway. And as we know, problems with one project can snowball for the whole project environment, leading to delays, cost overruns, or poor quality of the delivered goods.
4. Operational risks.
Operational risks refer to inefficiency or ineffectiveness of daily processes associated with project execution. For example, a lack of required resources, schedule delays, low productivity, etc. Inefficient and ineffective management processes.
Read more: How to Improve Operational Efficiency in Project-Based Organizations
5. Regulatory compliance risks.
This group of risks involves those events that cause the inability to comply with regulations or industry standards. This can also refer to a lack of required documentation or safety and environmental risks. When left unattended, these risks may lead to legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
6. External risks.
Finally, there have always been risks that are beyond an organization’s direct control. They may include market changes, supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, geopolitical issues, etc. These events are hard to predict, which emphasizes the need for preparing for contingencies and uncertainties.
Now that we know the main groups of risks managed by a project management office, let’s review the main steps of the risk management process.
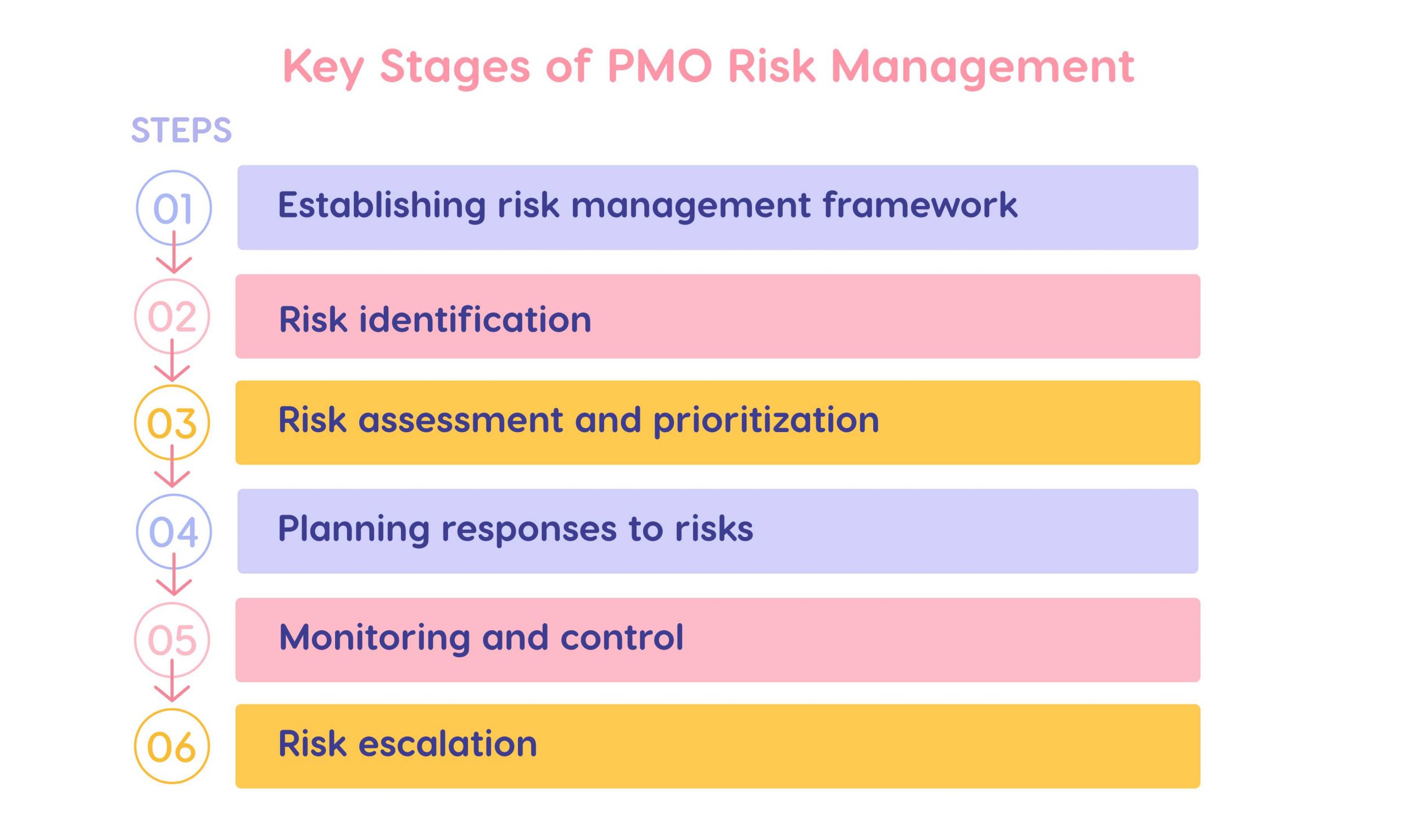
Key Stages of PMO Risk Management
The PMO risk management process is almost the same as project risk management. The difference is that it’s applied at the level of the entire portfolio or an enterprise, which means that the scope and focus of this process will be different. So, here are the key steps of the risk management process.
Step 1. Establishing risk management framework.
Before proceeding to the risk management process itself, a PMO should establish standards, approaches, and tools that this organizational department will use.
Step 2. Risk identification.
This step includes collecting risks from individual projects and programs, or other sources. Also, this involves the identification of interdependencies between projects and risks as well as detecting threats to the entire portfolio.
Read more: Creating a Risk Register: All You Need to Know
Step 3. Risk assessment and prioritization.
The next stage involves assessing each of the detected risks in terms of its impact and probability. This is followed by setting priorities between risks at the level of the entire portfolio. To achieve better results, PMOs can use different techniques and tools, for example, scoring models, Monte Carlo simulation, or What-if Analysis.
Step 4. Planning responses to risks.
And here comes the most important stage – determining what to do with all these possible threats and opportunities. As we know from traditional project risk management, there are several types of risk responses: mitigation, avoidance, transfer, and acceptance. The decision on selecting the most appropriate risk response plan should be made on the basis of risk analysis and a company’s organizational strategy – the selected action should be aligned with it.
Step 5. Monitoring and control.
PMO risk management is a continuous process, so it cannot be done once and forgotten. Regular monitoring and control help identify early warnings, signs of upcoming threats, or emerging opportunities. In all these cases, an organization will be much better prepared for dealing with risks effectively.
Step 6. Risk escalation.
Risk escalation means transferring a risk to the higher management level when it cannot be managed effectively in the current situation or requires broader decision-making or involvement of senior leadership. This is an important part of the PMO risk management process, which ensures that critical risks will be given required attention before threatening portfolio success or strategic objectives.
At first sight, these stages seem simple and manageable. But to make the PMO risk management more effective, let’s review some best practices that will help you succeed in this process.
PMO Risk Management: Best Practices and Recommendations
These recommendations will contribute to seamless and optimized PMO risk management.
1. Establish risk-aware culture.
Risk-aware culture involves encouraging transparency, communication, and responsibility for risks. It’s critically important for every stakeholder to communicate about risks without the fear of being blamed for them. Also, project team members should be aware of the importance of communicating potential threats as early as possible. Finally, both project participants and senior leadership should be aware of their roles in the risk management process.
2. Define roles and responsibilities.
Every risk should have an owner who will be responsible for tracking potential threats and won’t leave them overlooked. For example, project managers can be responsible to managing risks at the project level. A PMO monitors risks at the portfolio level. Senior executives make decisions on escalated risks and resource allocation for their mitigation.
3. Make risk management proactive, not reactive.
A proactive approach to PMO risk management is focused on anticipating risks, not just responding to them. This involves regular monitoring for detecting early signs of potential risks. Also, you can use scenario planning software for predicting risks, testing different ways to respond to them, and preparing contingency plans in advance. This proactive approach will eliminate unpleasant surprises and contribute to reducing negative risks and taking advantage of potential opportunities.
4. Conduct regular reviews.
As we’ve mentioned earlier, regular monitoring and control are an important component of the PMO risk management processes. Conduct reviews at both project and portfolio levels to detect emerging threats and check compliance with the required standards.
5. Leverage data analytics and technology.
Data-driven insights and software tools can become game-changers for the effective risk management practices. For example, project portfolio management tools or PMO tools, especially those equipped with predictive analytics, can predict possible risks and suggest risk mitigation strategies.
Let’s consider the role of software tools in more detail in the next section.
Tools and Technology for Risk Management in PMOs: Epicflow Example
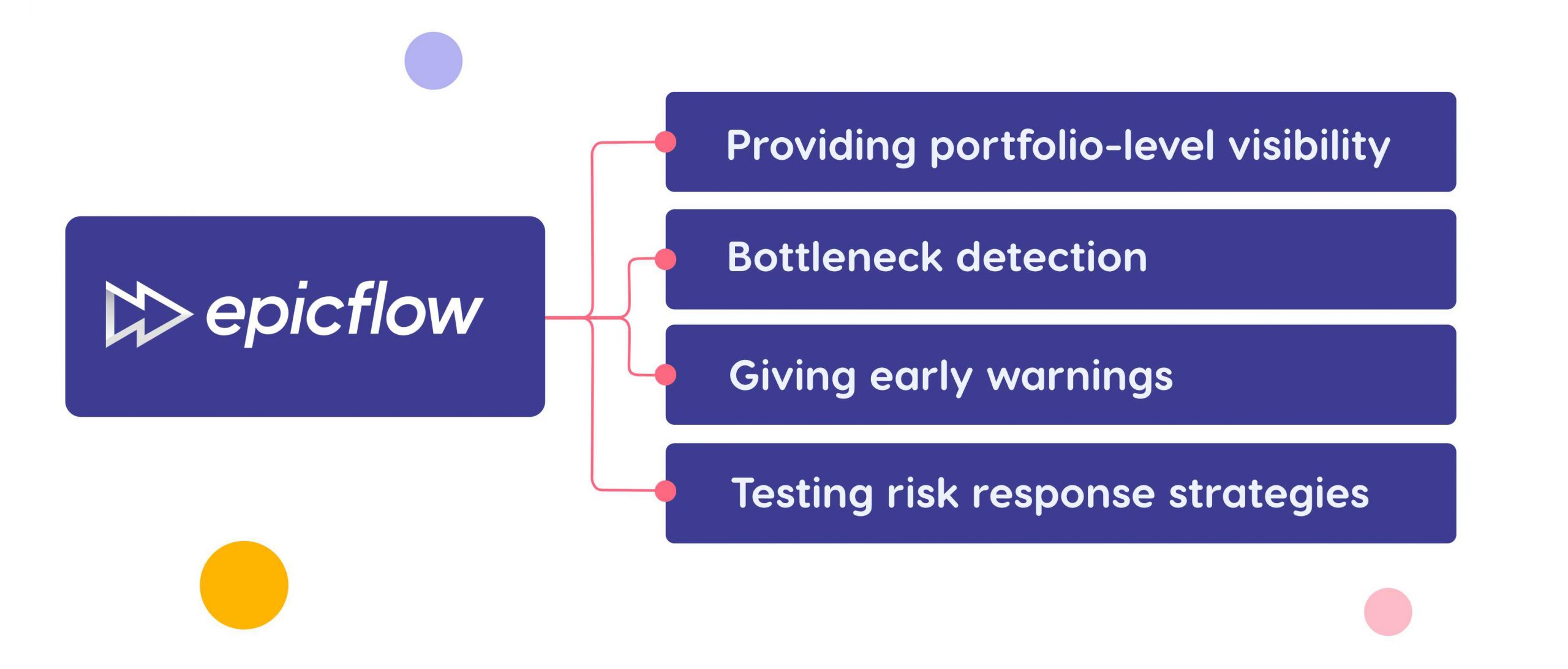
Typically, PMOs rely of different tools that help them manage projects, resources, and risks. In addition, they can use specfic risk management software, data analytics and BI tools, ERP systems, etc. We’d like to consider the contribution of software tool through the example of Epicflow. This is an AI-driven project resource management tool for complex multi-project environment with a shared resource pool. It’s designed to overcome the complexity of multi-project management and ensure successful multi-project delivery. And, of course, these benefits would be impossible without intelligent risk management functionality. So, how does Epicflow help PMOs manage risks?
Providing portfolio-level visibility
Epicflow allows you to track the state of the project environment from different angles. For example, you can check the state of all project portfolio and immediately see what projects are in red. Also, it budget management features show budget consumption so that you cannot overlook potential threats when it comes to project budget.
Bottleneck detection
Preventing and eliminating bottlenecks is one of the most important points in Epicflow’s philosophy. Epicflow’s capacity planning software predicts resources’ workloads and capacity, which helps detect future bottlenecks and take timely measures to mitigate them. This is how Epicflow supports a proactive risk management. Also, the tool helps identify the existing bottlenecks, find out their reasons, and apply strategies to eliminate them.
Giving early warnings
Epicflow’s capabilities are designed to warn users of possible threats in advance. In particular, its AI virtual assistant Epica can warn managers of upcoming bottlenecks and suggest how to fix the situation, which also contributes to a proactive and effective project and portfolio risk management process.
Testing risk response strategies
Epicflow’s AI-powered What-if Analysis allows you to try out different scenarios. By doing this, PMOs can find an optimum solution to potential or existing threats. In general, this feature serves as a solid support for informed decision-making.
Thus, leveraging Epicflow provides PMOs with necessary tools for proactive risk management and informed decision-making, especially when it comes to resource-related risks in complex multi-project environments. Book a call with our experts to learn more about Epicflow’s approach to successful multi-project, resource, and risk management.
Final Thoughts
Poor risk management is wasteful for today’s organizations running multiple concurrent projects. Obviously, it leads to missing deadlines, exceeding budgets, and even project failures. Fortunately, proper risk management performed by a project management office can change the game: it standardizes risk management processes, provides visibility into the whole project environment, and facilitates more effective decision-making. Organizations adopting PMO risk management have an opportunity to minimize losses, improve portfolio performance, and gain strategic advantage.
References
- Bill for government projects at risk of failure doubles to £200bn. The Times. Retrieved from: https://www.thetimes.com/uk/politics/article/major-government-projects-risk-failure-z37stbm3q
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PMO risk management?
PMO risk management involves managing risks at the level of a Project Management Office (PMO): identifying, assessing, monitoring, and mitigating risks across projects, programs, and portfolios.
Why is risk management important for PMO?
With effective risk management, PMOs can prevent project failures, optimize resource utilization, ensure strategic alignment, and improve project delivery and portfolio performance.
How does a PMO help manage project and program risk?
The main pillars of PMO risk management, which help this organizational unit add value to an organization, are providing governance, ensuring visibility and strategic alignment, supporting decision-making, and promoting stakeholder engagement.
What are the most common PMO risks?
The most common risks that a PMO has to deal with include strategic risks, operational risks, finacial risk, technical risks, compliance risks, and external risks.
What are the best practices for PMO risk management?
For effective risk management in PMO, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Create a risk-aware mindset;
- Determine clear roles and responsibilities;
- Take a proactive, not reactive approach to risk management;
- Perform regular reviews and analysis;
- Leverage software with predictive capabilities, e.g., project portfolio management tools.
What are the key stages of PMO risk management?
The main stages of PMO risk management involve determining the risk management framework, identifying risks, assessing and prioritizing them, planning mitigation strategies, monitoring and controlling, and escalating risks when necessary.
What is risk escalation in PMO risk management?
Risk escalation in PMO risk management means transferring a risk to the higher management level. It becomes necessary when it cannot be managed effectively at the current level or poses a threat to to a company’s objectives.
What is the difference between project risk management and PMO risk management?
Project risk management is performed at the level of individual projects. PMO risk management has a broader scope: it manages risks at the multi-project level, which means that it takes into account project interdependencies and an organization’s strategic objectives.
What tools support PMO risk management?
Project management offices often use project portfolio management systems or PMO software, risk management solutions, ERP or BI platforms. It’s a big advantage if a software solution has AI-powered functionality, e.g., scenario planning.